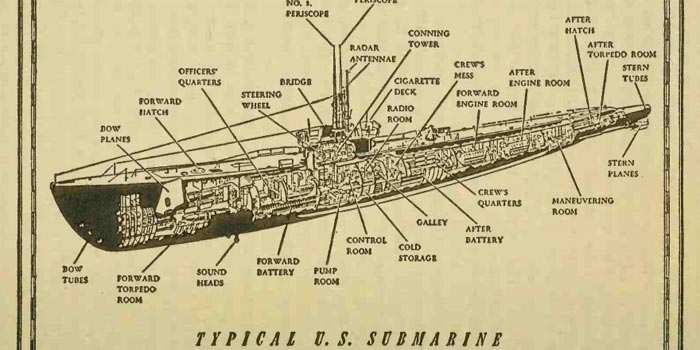
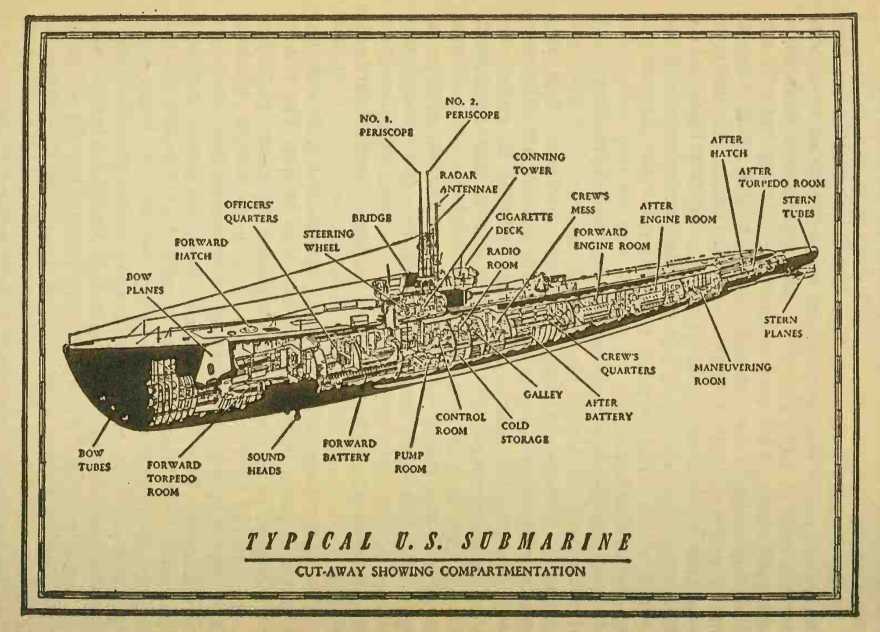
Hi everyone. This is Sune. Morgane is overworked again. As such I will answer the questions that have come up that mostly fall under my specialty.
If Japanese shipgirls aren’t kami do they see themselves as kami?
Most do not. One does but she should not be taken seriously.
Where are the other Japanese shipgirls?
Pacific’s focus is on American shipgirls and their friends. Japanese shipgirls only appear when they make sense in Pacific’s overall storyline or have important roles to play.

I am too lazy to retype all of that.
Thank you for your comments.
The main volume Pacific character design process moves roughly in chronological order. We are somewhere around Midway and Santa Cruz right now. The contributions you mention by the British Pacific Fleet occurs in 1944. This is well after America established naval dominance through systematic attrition, superior shipbuilding, capable development of novel naval battle tactics, and an overall strategic vision that we lacked.
Personally I have no impression whatsoever of Royal Navy capabilities. In Japan among naval enthusiasts they are famous for suffering crippling defeats at the hands of the Imperial Navy in 1941 and 1942. In fact from my own (Japanese) sources it is understood that the British only joined in the Pacific War for fear that America would free up their former territories and colonies. In any case a general sentiment in Japan is that we lost (or in the words of our prime minister “the war ended”) to America and not the Allies.
If the contributions of the British are very significant then unfortunately I do not know about it. We are happy to learn more about it but the matters of the Royal Navy rarely come up within team discussions. Without knowing anything about the Royal Navy we obviously cannot create shipgirls that would be a good and faithful depiction of the actual history.
Furthermore. There is no one on the Pacific team who works on the Royal Navy. Not since our British person retired years ago. Without someone to advocate for British characters it is unfortunate but inevitable that they get pushed back further and further on the illustration schedule.
By the way Morgane is an anglophile who loves many things that are British. She has a degree in Arthurian and Celtic legends. She is also very knowledgeable in the roles that were played by the Royal Air Force in the Battle of Britain and the European theater. However Morgane is busy working on everything else. As such the British shipgirls that she has created are relegated to background status and once again do not get drawn.
The reason why the Soviet characters get drawn first is that there are people who are actively working on them. Furthermore given Pacific’s world building the USSR remains a dominant power. Without anyone working on the resurgent British Empire it is natural that foreign shipgirl art tend to prioritize those that the team are interested in.
We are very sorry.
——-
And now actual content.
I want to do a Fireside Chat too. Should I title it that?
Despite my reputation for being the one who provides fanservice I also provide significant cultural elements into all of our shipgirl designs. For the Japanese shipgirls that come into Pacific I want to make their “Japanese-ness” explicit. In other words rather than drawing from contemporary Japanese culture such as the high school uniform or the school swimsuit I draw almost all of my inspiration from traditional and ancient Japanese culture.

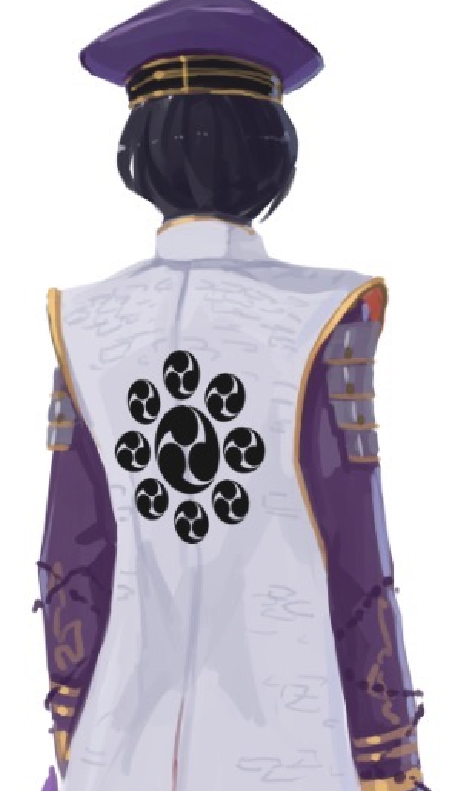
There are certain character attributes that are immediately recognizable by those familiar with the references. As such my Japanese shipgirl designs draw liberally from all sources. For instance below.
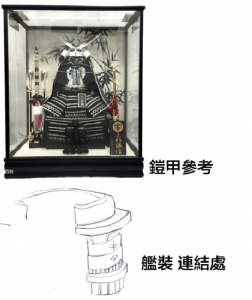
The armor pattern of this particular shipgirl is not simply that of the approximate shape to what her turret mounts would be. Given her namesake’s region I thought it prudent to provide Sima with reference images of an iconic individual from said region. As such you can see that specific armor pattern weaved into her clothing design.
A great deal of the Japanese shipgirl’s personality comes out of a composite of their histories, crew, historical performance and the like. However much like how American shipgirls in Pacific exemplifies certain aspects of America the Japanese shipgirls do so as well. For example because of its association with Japanese faith and primitive religion Pacific’s Kumano is a reserved and calm individual. She is not very similar to her KanColle counterpart in that regard who makes funny howling cat noises during attack. In the example above the shipgirl is heavily associated with winter due to the magnificence of the wintery frost that appears every year.

An example of this is preserved in art as you can see above. With this theme her personality writes itself. Someone who is outwardly cold but like the joys of winter is warm inside. This aspect symbolizes the part of Japan in which she is named after and it superimposes over any “ship” part that is her.
Afterwards it is my honorable duty to make the shipgirls sexy. I have never understood the prudishness that some of our western readers exhibit.
Seriously. They are shipgirls. GIRLS. DO I NEED TO SAY ANYTHING ELSE.
ALSO I’M BORED NOW.
SEE YOU NEXT TIME.